In my last blog post we deployed a single ECS host with access to GPU. We can utilise a GPU to speed up our computer vision tasks by 10x when using a GPU compared to using CPU. This can be critical for real-time operations such as blurring faces in monitoring displays or annotating real-time videos from drone footage. In the previous blog we noted a weakness in the solution, in that only a single task could be run on each host as there was only a single GPU for the AWS EC2 instances type. EC2 instance type g4dn.xlarge used in the previous blog post had 4 vCPU, 16 GB memory and a single GPU. Tasks were set up to share memory and CPU from the host but could not share the single GPU with another task. To enable GPU sharing, several changes are required:
- Add an environment variable to the task definition
- Update the ECS host userdata to enable GPU sharing
- Remove resource requirement in the task definition
The code changes are shown below:
Added environment variable ( line 36 – 39)
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "main" {
family = "${var.app_name}-task-definition"
network_mode = "awsvpc"
requires_compatibilities = ["EC2"]
cpu = var.container_cpu
memory = var.container_memory
task_role_arn = aws_iam_role.ecs_task_role.arn
execution_role_arn = aws_iam_role.ecs_task_execution_role.arn
container_definitions = jsonencode([
{
name = "${var.app_name}-container"
image = "${aws_ecr_repository.repo.repository_url}:latest"
essential = true
cpu = var.container_cpu
memory = var.container_memory
environment = [
{
name = "TZ",
value = "Pacific/Auckland"
},
{
"name" : "ENVIRONMENT",
"value" : terraform.workspace
},
{
"name" : "AWS_REGION",
"value" : data.aws_region.current.name
},
{
"name" : "APPLICATION",
"value" : var.app_name
},
{
"name" : "NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES",
"value" : "all"
}
]
logConfiguration = {
"logDriver" = "awslogs"
"options" = {
"awslogs-group" = aws_cloudwatch_log_group.ecs_task.name,
"awslogs-stream-prefix" = "ecs",
"awslogs-region" = data.aws_region.current.name
}
}
mountPoints = [
]
}
])
tags = {
Name = "${var.app_name}-task"
}
}
Update userdata in locals block
locals {
ecs_userdata = <<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
cat <<'DOF' >> /etc/ecs/ecs.config
ECS_CLUSTER=${aws_ecs_cluster.main.name}
ECS_AVAILABLE_LOGGING_DRIVERS=["json-file","awslogs"]
ECS_LOG_DRIVER=awslogs
ECS_LOG_OPTS={"awslogs-group":"/aws/ecs/${var.app_name}-ecs-cluster","awslogs-region":"${data.aws_region.current.name}"}
ECS_LOGLEVEL=info
ECS_ENABLE_GPU_SUPPORT=true
DOF
sed -i 's/^OPTIONS="/OPTIONS="--default-runtime nvidia /' /etc/sysconfig/docker && echo '/etc/sysconfig/docker updated to have nvidia runtime as default' && systemctl restart docker && echo 'Restarted docker'
EOF
}
Remove resource requirement in the task definition
resourceRequirements = [
{
type = "GPU",
value = "1"
}
]
After implementing these minor changes, we performed tests on two simultaneous tasks.
Testing
Create an ECS Task with the following parameters:
- Cluster – ecs-gpu-cluster
- Launch type – EC2
- Desired tasks – 2
- Networking VPC – ecs-gpu
- Networking subnets – private subnets only
- Networking security group: ecs-gpu-ecs-host
In due course, you will observe two tasks running in the console, simultaneously sharing the single GPU.
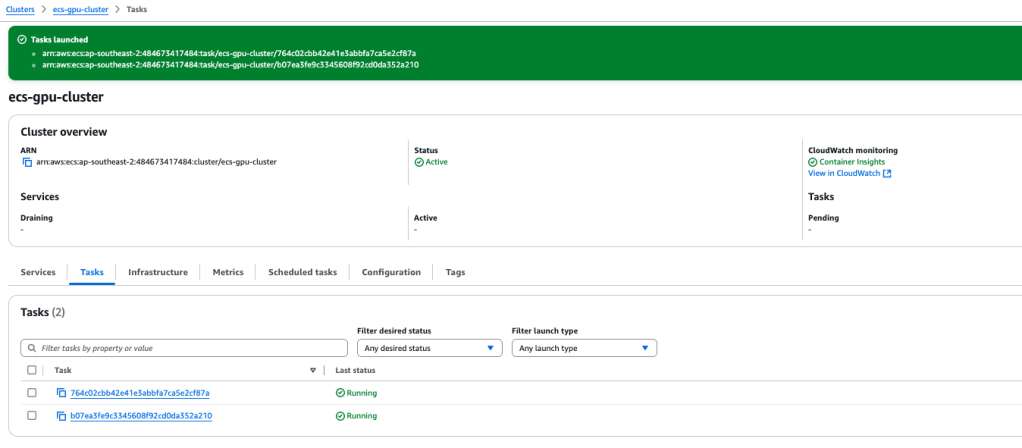
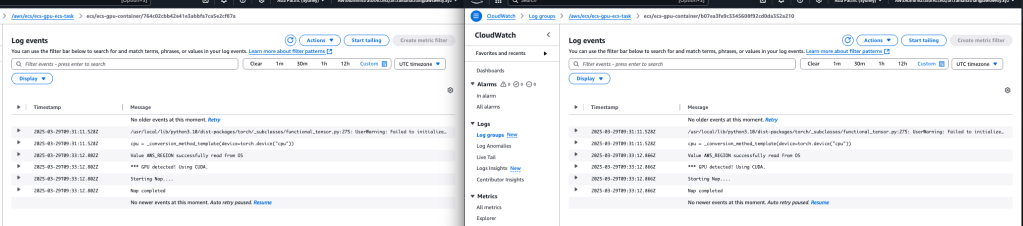
In Cloudwatch, there will be an ECS task Loggroup, featuring a Log Stream for each task. This will allow you to monitor both tasks running concurrently, while accessing the GPU at the same time.
However, a potential issue may arise when the ECS host has initiated or is running several tasks and yet does not have adequate CPU or memory capacity to kick off another task on the same ECS host. Fortunately, AWS has an ECS feature called ‘Capacity Provider’ which will facilitate the ECS host scale-out and scale-in processes. The ECS Cluster Capacity Provider can be integrated with our ASG and be triggered via CloudWatch Alarms.
The code for Capcity Provider and Cloudwatch Alarms is shown below:
resource "aws_ecs_capacity_provider" "hostecs_cp" {
name = "hostecs-capacity-provider"
auto_scaling_group_provider {
auto_scaling_group_arn = aws_autoscaling_group.ecs_hosts.arn
managed_scaling {
status = "ENABLED"
target_capacity = 50
maximum_scaling_step_size = 1
minimum_scaling_step_size = 1
}
}
}
resource "aws_ecs_cluster_capacity_providers" "ecs_cluster" {
cluster_name = aws_ecs_cluster.main.name
capacity_providers = [aws_ecs_capacity_provider.hostecs_cp.name]
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "scale_out" {
name = "ecs-gpu-scale-out"
autoscaling_group_name = aws_autoscaling_group.ecs_hosts.name
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
scaling_adjustment = 1
cooldown = 60
policy_type = "SimpleScaling"
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "scale_in" {
name = "ecs-gpu-scale-in"
autoscaling_group_name = aws_autoscaling_group.ecs_hosts.name
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
scaling_adjustment = -1
cooldown = 60
policy_type = "SimpleScaling"
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "cpu_high" {
alarm_name = "ecs-cpu-high"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanThreshold"
evaluation_periods = 2
metric_name = "CPUUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/ECS"
period = 60
statistic = "Average"
threshold = 75
dimensions = {
ClusterName = aws_ecs_cluster.main.name
}
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.scale_out.arn]
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "cpu_low" {
alarm_name = "ecs-cpu-low"
comparison_operator = "LessThanThreshold"
evaluation_periods = 2
metric_name = "CPUUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/ECS"
period = 60
statistic = "Average"
threshold = 30
dimensions = {
ClusterName = aws_ecs_cluster.main.name
}
alarm_actions = [aws_autoscaling_policy.scale_in.arn]
}
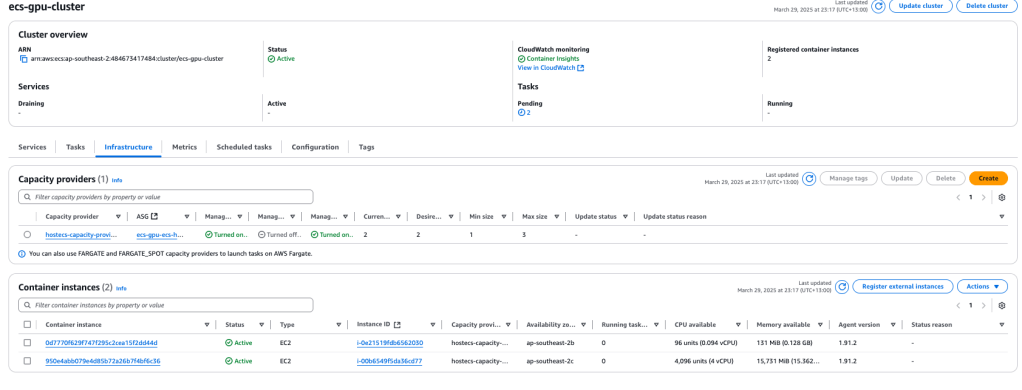
Testing again with two concurrent tasks will cause the ASG to create a 2nd EC2 ECS instance. Note the one instance (instance i-0e21519fdb6562030) has insufficient capacity to start another task but instance I-00b6549f5da36cd77 still has full capacity to cater for two additional tasks.
In this blog, we updated our previous code to allow GPU sharing amongst tasks and automatic provisioning of more EC2 ECS resources when the current cluster reached high utilisation. The solution will also scale-in resources when the utilisation drops. The scale-in and scale-out processes are achieved using AWS CloudWatch alarms and adjusting the ASG auto-scaling policy. These improvements deliver significant benefits: GPU sharing maximises hardware utilisation and reduces costs by allowing multiple workloads to run concurrently on a single GPU instance, while the dynamic scaling ensures optimal resource allocation providing capacity when needed and eliminating waste during periods of low demand. Together, these enhancements create a more cost-effective, responsive, and efficient infrastructure for GPU-accelerated computer vision tasks. The full code (including the updates for GPU sharing and scale-in/out) can be found at https://github.com/arinzl/aws-ecs-with-gpusharing.

